Retinal Tear & Detachment
If the vitreous pulls very strongly against one area of the retina when it separates, the retina may tear. This may cause the patient to experience floaters and flashing lights. If the tear takes place across a blood vessel, bleeding within the vitreous may occur causing even more floaters, spots and “cobwebs.” A retinal tear can lead to the development of a retinal detachment. Retinal tears that cause symptoms should be treated to decrease the chance of developing retinal detachment.
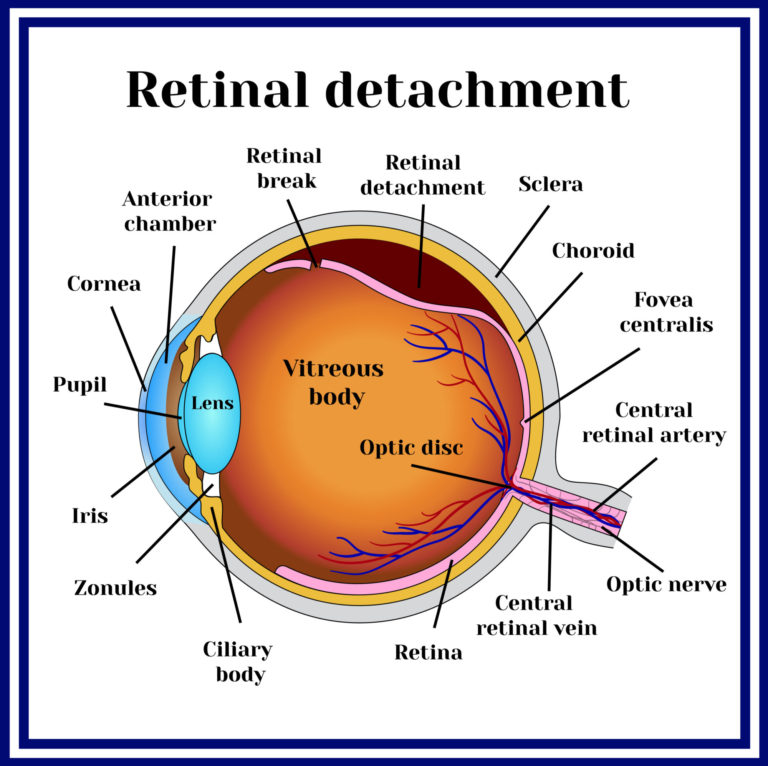
Retinal Detachment
If a retinal tear develops, fluid may get under the retina, which is the sensory tissue that lines the back wall of the eye. Think of the retina as a thin layer of tissue on the inner back wall of the eye, much like wallpaper is a layer on a wall. Once fluid gets under it, the retina comes loose from the back eye wall, and this is called a retinal detachment. At this point, patients generally experience a shadow coming over their vision. This is a potentially blinding condition, but fortunately it can be treated in most patients. In certain diseases, the retina can pull away from the back wall of the eye without a retinal tear as the cause. Usually these conditions can be treated as well.
For more information, visit the American Academy of Ophthalmology Eye Health resources at: https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/detached-torn-retina